How can consumer wearable technology drive innovation in medical devices?
Even in turbulent market dynamics, wearable devices continue to grow throughout the world. The main market players' respective market share may increase or decrease, but at a macro level, growth is still strong – the IDC report shows that sales in 2016 exceeded 100 million units, up 25% from 2015.
In the long run, the technology used in these devices has been innovated over the past 20 years. Not long ago, the ECG chest strap was still advanced technology, and then had a "wearable" function. Since then, we have seen GPS, accelerometers, gyroscopes, optical biosensors, skin current response sensors, etc. integrated into a variety of wearable devices.
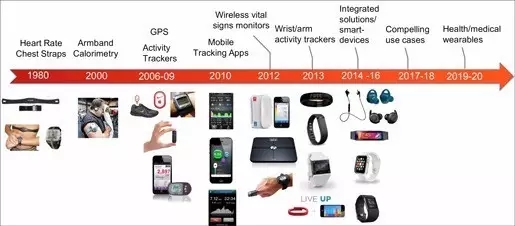
These technologies have brought a new user experience, mainly in the field of wearable devices such as sports and fitness tracking. However, new advances in wearable technology, especially biosensor systems, open up new possibilities for the application of wearable devices in medical health and medical devices. In fact, according to Frost & Sullivan's forecast, by 2020, the market for clinical-grade medical wearable devices for chronic disease management and other clinical applications will reach $18.9 billion, a compound annual growth rate of 29.9%.
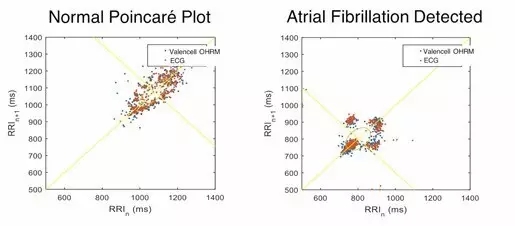
This has become a reality as the performance levels of wearable optical sensor systems in medical cases are being validated. For example, there has been data indicating that embedded biometric sensor systems in consumer wearable devices can detect the presence of atrial fibrillation. This is done by measuring and analyzing the R-R interval, the time between heart beats, to show different patterns of healthy and unhealthy hearts.
The left picture below is a healthy heart, showing the shape of a "torpedo" from the bottom left to the top right, while the cluster shown on the right is at the bottom left of the picture, which clearly indicates atrial fibrillation. The data in these charts was collected by consumer-grade audio earbuds with advanced biometric technology to measure heart rate and R-R interval. The importance of ear rhythm monitoring is that it can perform monitoring very accurately (based on the principle of high perfusion and low motion artifacts associated with ear position) and is truly mobile (embedded in earwear that people use everyday) .
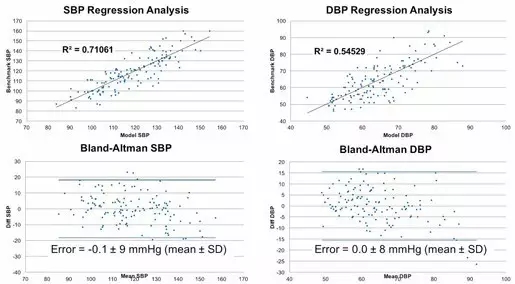
Another example is blood pressure. Advanced optical biometric sensors similar to those found in consumer wearable and audible devices have proven to be comparable to consumer-grade blood pressure cuffs. Valencell is conducting an ongoing study in which we collected hundreds of sets of data from more than 100 different research participants divided into optical biometric sensors and blood pressure cuffs. The results were convincing. of.
NINGBO MEDICAL EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.techartmeds.com