High-yielding Cultivation Technique of Grafted Watermelon in Winter and Spring
1 Variety selection and determination of seeding grafting time
1.1 Variety selection?
Scion generally choose to grow fast in low temperature conditions, with strong affinity of rootstock grafting, melons can normally enlarge and mature, excellent quality of early maturing varieties, such as medium-sized watermelon 8424, Jingxin 1, etc., small watermelon bit, early spring ruby, Wan Fulai , Tianci 208, Little Angel, Xiaolan and so on. The rootstock varieties should be matched with the type of watermelon. Generally, the growth potential of small watermelons is weaker. The rootstocks should be selected from the weaker varieties of gourds, such as FR Shentongli and Huazhong No.2; medium-sized watermelons can be selected from stronger rootstock varieties. Such as Chaofeng F1, picking gourd anvil and other varieties. ?
1.2 The sowing date is determined?
Determine the sowing date according to the conditions of the insulation of the facility, the management level, and the planned time for the listing of the watermelon. Generally, the seedling period of grafted watermelon in winter is about 50 days. Insulation facilities such as 3 sheds and 4 membranes (ie, greenhouses, middle sheds, sheds, and plastic mulches) are planted in special early-maturing plants and planted in mid-late and late New Year's Day in December and in February. Planting in the middle of the first half, generally listed before and after the end of April; greenhouses + greenhouses + film cultivation, sowing in mid-January, planting in late February, generally listed in early May. ?
2 Grafting seedlings for cultivation or purchase?
The cultivation of grafted seedlings of watermelon in early spring is focused on controlling the seedbed temperature. It can be controlled by heating and ventilating the electric heating line. The minimum temperature of the seedbed should not be lower than 15°C to ensure the healing of the grafted seedlings. About 25 days after grafting, when grafted shoots have 3 to 4 true leaves, colonization can be performed. Can also be grafted to the point of supply of seedlings grafted to survive the age of seedlings for colonization. ?
3 Colonization?
3.1 Preparation before planting?
Before planting, soil preparation, fertilization, and cropping should be performed. Compared with self-root watermelon, grafted watermelon can be applied with 15%-20% basal fertilizer. The basal fertilizer should use organic fertilizer such as vegetable cake and duck mud to improve the quality of the grafted watermelon. For every 667m, 2 cooking cakes about 100kg, or duck mud 2000 ~ 2500kg, plus 30 yuan compound fertilizer, potassium sulfate 15kg. The basal fertilizer is evenly applied to the ground, and then deep-turned about 30cm, the pupa into a bow-shaped, generally 6m wide standard shed to do 2 æ (crop cultivation to do 4-5 畦). After the site preparation, the entire shed was covered with mulch, a small and medium arch shed was erected, and the greenhouse was closed. The sunlight was used to raise the temperature in the interior. ?
3.2 timely planting?
The time for colonization using a 4 membrane covering was generally mid-to-mid-February, ie when the soil temperature of the colonization shed rose above 12°C. Grafting seedlings should not be planted too deep, grafting incision must be higher than the ground 1 ~ 2cm, can not touch the soil. The colonization density is slightly thinner than that of the self-rooted watermelon. In greenhouses, medium-sized melons (such as 8424) are planted with 250-350 strains per 667 m2, and small melons (such as genomics) are planted with 400-600 strains per 667 m2. The medium-sized melons cultivated by arranging are planted at about 800 per 667m?, and the small watermelons are planted at about 1200 per 667m?. ?
4 Field management?
4.1 Untwist or clip.
Watermelon seedling grafted by grafting method (except top inserting method) can be untied or clipped 5 to 7 days after planting. If you go too early, the wound has not completely healed well, and the scion is easy to fall off; if it is too late, lines or small clips will get into the hypocotyls, which will affect the growth of the melon seedlings. Detachment line or clip should be carried out in the sunny, can not withstand the low temperature cold weather weather solution line or clip, to prevent freezing, scion fall.
4.2 Remove Adventitious Buds from Rootstocks?
Remove adventitious shoots of rootstock in time to avoid affecting the growth of scion. ?
4.3 Shed temperature control?
Watermelon is a hi-light thermophilic crop. The whole growth period is dominated by high temperature and adequate light management. Colonization to the live tree stage, closed shed film, high temperature and humidity promote new roots and live trees, in the cold wave, the evening shed to add insulation measures, beware of the emergence of a frozen seedlings. Live tree till the extension of the vine, the temperature of the shed is controlled at about 30°C. Generally, the shed is first uncovered, and then the greenhouse is exposed for ventilation. From early flowering to fruit setting, the temperature is controlled at about 25°C to control the growth rate and promote the transformation from vegetative growth to reproductive growth. With the increase of the outside temperature, the ventilation opening is gradually increased to reduce the humidity in the shed. After fruiting, raise the temperature of the shed to 30°C to promote fruitful expansion. When the fruit is of a certain size (about 1 kg), the temperature difference between day and night is gradually increased, and the fruit quality is improved. ?
4.4 Pruning leads?
Grafting watermelon greenhouse precocious cultivation, generally using 3 vine pruning, a main side of the cranberry, the rest of all knocked out, and promptly straighten the vine, so that the vines in the pod surface to maintain a certain angle of oblique growth. After waiting for fruit, let the offspring grow, increase the leaf area coefficient, and promote fruit enlargement. And the use of female branches on the branches of the female flower set fruit, forming two loquat melon. The second pods were harvested and shredded in time to remove the diseased side branches and diseased leaves. The third pod and four pods were formed on the new offspring of the main vine and the vine. One of the main side vines was trussed and draped with U-shaped tying method. The vines were put on the shelves so that they could be tied with the length and tied at intervals of 4 to 5 knots. After the 2 vines were set, they were topping to facilitate ventilation. , to promote the growth of fruits, the other side of the vine is crawling to stay on the surface, increase the base leaf area, and promote the growth of the underground part.
4.5 pollination fruit set?
Watermelon belongs to the female and male flowers of the same plant. It is rare that there are bisexual flowers of the same sex. In addition to sex flowers, other female flowers need to rely on insect pollination in order to set fruit under natural conditions. Because the watermelon planted in the greenhouse was planted in the middle and late March, the temperature is still relatively low, and the insect activity is small. In addition, the rate of pollination by the insect vector and the airborne medium is reduced due to the cultivation in the shed. Therefore, artificial supplementary pollination must be performed to ensure fruit set. Artificial pollination is usually in the morning, on the opening day of female flowers, male flowers are applied to female flowers, or male flowers are smeared with a soft-hair pen and male flowers. After the pollination, a mark is attached and the pollination date is indicated so that the ripe melon can be harvested in batches according to the number of days after the pollination. The fruit-setting section should be held in the 12th to the 25th section. Before the 10th section, it should be removed as soon as possible. Otherwise, the watermelon may be hollow or smelly after it matures. When the first gourd was about 1 kg, the second batch of female flowers was pollinated artificially to cultivate the second gourd. When the melon has the size of the egg, the fruit is thinned, and the melons of the positioning melon are dried and the melons are harvested. The cultivated watermelon is hung on the vine, and when the melon swells to a certain weight, it is easy to break the vine or the stalk is broken. The method of hanging the melon can be used to make a tight knot on the mullion with a wide knitting silk rope, and then the melon can be hung on the melon shank, and the melon can be knitted into a mesh bag and can be knitted by the condition. ?
4.6 fertilizer management?
Grafted watermelons are more hi wet than self-rooted watermelons. After planting live trees, it is appropriate to apply 100 times compound fertilizer for 2 to 3 times. In the vine extension period, depending on the weather conditions and plant growth, the top dressing should be applied in an appropriate amount, and phosphorus and potash fertilizers should be used. Partial application of nitrogen fertilizer should be avoided. After the melon seedlings come out of the vine, they are no longer easily topdressed before fruit set. Into the expansion of the guaranty period, according to the growth of the plant watering fertilization, 15 ~ 20cm from the root to play a fertilization hole, interval 7 days, with 0.6% potassium sulfate compound fertilizer pouring 2 or 3 times; later with the concentration of 0.2% potassium dihydrogen phosphate was sprayed on the leaves for 2 to 3 times to increase the sugar content of the fruits and improve the quality. After harvesting each pod, each 667m2 of 15kg of ammonium bicarbonate plus 15kg of superphosphate dilute 30 doubling holes to promote the growth of the melon.
4.7 Prevention of acute blight
Watermelon grafted seedlings with gourd rootstocks are susceptible to physiological acute blight disease in fruit setting. Therefore, excessive pruning should not be used to avoid poor root growth. At the same time pay attention to the balanced supply of water, especially when the drought does not cause the water to wither. ?
4.8 Disease Prevention?
Grafting watermelon seedlings is mainly able to prevent the occurrence of soil-borne diseases such as watermelon wilt disease, and it is still necessary to strengthen prevention and control of diseases such as spot disease, bacterial blight, and powdery mildew. Leaf blight, spot disease, and leaf blight can be used 58% Lei Duomi manganese zinc wettable powder 600 times, 70% thiophanate-methyl wettable powder 1000 times, 50% carbendazim wettable powder 600 times liquid , 75% chlorothalonil WP 600 times liquid spray disease prevention. Powdery mildew can be treated with 10% Shi Gao WP 1500 times, 40% Fuxing EC 6,000 times, 25% Triadimefon 1500 times liquid spray control. ?
4.9 Pest Control?
The pests mainly include ground tigers, aphids, leafhoppers, thrips, melons, yellow slugs, and Spodoptera litura. The control of aphids, leafhoppers, and thrips can be achieved by spraying 20% ​​of 20% by imidacloprid wettable powder and 2500 times by 1% of insecticidal cream. The control can be sprayed with 25% of 5% fipronil suspension. Spodoptera litura can be sprayed with 15% of the EC 4000 times liquid, 10% of the suspension agent 1500 times. ?
5 Harvesting?
According to the maturity of different varieties, timely harvest. Generally, the grafted watermelon in the greenhouse is more difficult to be observed or matured by the sound of shells, and the pollination timing method is used to identify the maturity of the fruit. Can be harvested separately by date. Grafting watermelon should not be harvested earlier than ripe, generally 2 to 3 days later than the root watermelon harvest. Grafted watermelon melon shape is too large, single fruit weight slightly higher than the self-root watermelon, 667m2 yield up to 3000kg or more.
An anesthetic (or anaesthetic) is a drug to prevent pain during surgery, completely blocking any feeling as opposed to an analgesic. A wide variety of drugs are used in modern anesthetic practice. Many are rarely used outside anesthesia, although others are used commonly by all disciplines. Anesthetics are categorized into two classes: general anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of consciousness, and local anesthetics, which cause a reversible loss of sensation for a limited region of the body while maintaining consciousness. Combinations of anesthetics are sometimes used for their synergistic and additive therapeutic effects. Adverse effects, however, may also be increased. We produce anesthetic raw materials like tetrcacain, lidocaine prilocaine. These three anesthesia products are in commercial quantity.
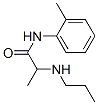
Prilocaine structure:
Tetracaine Anesthetic Drug,Anesthetic Powder,Anesthetic Cream Pharmaceuticals,Bupivacaine Base Anesthetic Pharmaceuticals
Jinan Jianfeng Chemical Co., Ltd. , http://www.pharmachemm.com