SuperMaze animal behavior video analysis software principle and application field
2021-08-04 06:21:31
SuperMaze animal behavior video analysis system principle and application field
SuperMaze Animal Behavior Track Analysis Platform is a universal motion track record analysis system that uses image processing technology to automatically track and record animal activities through video cameras and computers. It can be applied to neuropharmacology, learning memory pharmacology, anti-aging pharmacology and new drugs. General pharmacological and toxicological studies of the nervous system can also be used in basic research in neuroscience.
SuperMaze is suitable for Morris water maze experiment, opening experiment, open field experiment, spontaneous activity, darkness test, T-maze, Y-maze, radial maze, elevated cross maze, eight-arm maze, Barnes maze, conditional position preference experiment Various animal experiments such as Zero Maze, Hole Experiment, Platform Experiment, and New Object Recognition.
In addition to the basic functions of automatically tracking and recording animal activity trajectories, SuperMaze also has various animal behavior events, trajectory data import and re-analysis, experimental data management and real-time recording functions that can not be automatically recognized by the video system through the event recorder, and can receive 16 external input signals, controlling 12 external output signals, fully demonstrate the advantages of combining automation and flexibility.
SuperMaze is easy to set up, flexible, and has a high performance-price ratio.
System functions
â— Freely designed platform area graphics (platform software open) for various behavioral experiments
â— Stable and reliable head, middle and tail tracking algorithm, even identifying Drosophila larvae
â— It can collect and process various behavioral data in animal active behavior, learning memory, conditioning, reactivity, and passive behavior.
â— Original event statistics and analysis functions, the results of the experiment are clear at a glance
â— Visualized experimental data management function, safe and convenient
â— Powerful comprehensive reporting and support for one-click export
â— Flexible experiment start and end methods to improve experiment efficiency
â— Built-in convenient and fast manual event recorder to record various behavior characteristics of animals
â— Customize the animal's attribute template, the experimental parameters are more comprehensive
â— Complete software expansion, supporting up to 16 channels of experimental analysis
â— The controller can be compatible with instruments from well-known foreign behavioral manufacturers.
Application field (experimental experiment)
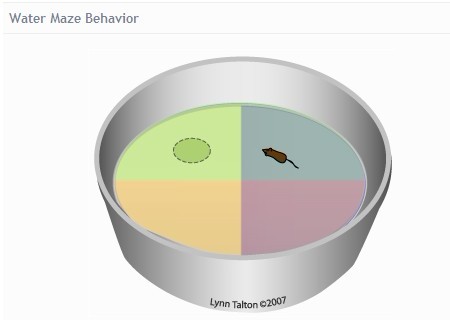
1. Morris water maze (MWM)
The Morris Water Maze Experiment is an experiment in which forced experimental animals (rats, mice) swim and learn to find platforms hidden in the water. The Morris water maze is mainly used to test the sense of spatial position and direction of the experimental animals (spatial positioning). Learning and memory skills are widely used in learning and memory, Alzheimer's disease, hippocampus/external hippocampus research, intelligence and aging, new drug development/screening/evaluation, pharmacology, toxicology, preventive medicine, neurobiology, animal psychology and behavior. The fields of biology and computer-assisted instruction in many disciplines such as biology have been widely recognized in the world, and are the preferred classical experiments for medical institutions to conduct behavioral research, especially learning and memory research.
2. T-maze experiment (T-maze)
The T labyrinth consists of one stem and two arms. The maze gives the animal no reference when it comes to getting food rewards. It can only be selected according to self-judgment. The food intake is generally limited a few days before the test, and the animals are trained 2 days before the test. After the formal test, the test was conducted 15 times a day, each test interval of 1 min, a total of 3 d.
The subject is placed in the base of the "T". Following a short delay, it is allowed to explore the maze and choose to enter either the right or left arms. The choice is scored according To variety of criterion, including spontaneous alternation, cued reward, or to indicate a preference. Based on the criterion used in an experiment, the T-maze can be used to test learning and memory, preferences for stimuli or reward, or spontaneous alternation behavior .
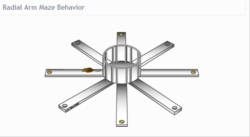
3. Eight-armed maze (Radial Arm Maze)
Subjects are placed in the center of an eight-arm radial maze. Four possible chosen arms are baited with food pellets in opaque containers. The subject is given the opportunity to visit all the arms and collect all the available food pellets. After a rentention delay In win-stay conditions, the same four arms are baited, and the number of correct choices the subject makes in collecting the pellets is recorded. In win-shift conditions, the four arms NOT baited in The earlier trial are now baited, and the number of correct arm choices is recorded. Each day, a new set of four arms is chosen randomly.
The eight-armed maze is used to detect the learning and memory aspects of a drug or brain damage. It consists of eight identical arms that radiate from a central platform, so it is called the end of each arm of the radiation labyrinth. There are food supply devices. According to the strategy of analyzing animal feeding, the number of times, time, correct number, number of errors, route and other parameters of entering each arm can reflect the spatial memory ability of the experimental animals. Relatively speaking, the eight-arm maze is simple and feasible to operate, and can distinguish between short-term working memory and long-term reference memory. It has been widely used for learning memory function evaluation.
4. Independent activities, open field experiments ( Open Field )
The subject is placed in the activity chamber for a specified time period. Activity levels and movement in three dimensions are recorded by the activity system and can be analyzed for evidence of hyperactiviy, hypoactivity, anxiety, explorative behaviors, and stereotyped rotation.
Spontaneous activity market field analysis system is to observe the neuromuscular changes of experimental animals and various behaviors after entering the open environment, such as animals' fear of new open environment and mainly activities in the surrounding areas, with less activity in the central area, but animals The nature of inquiry also motivates them to generate motivations for activities in the central region, as well as to observe the resulting anxiety. Central stimulant drugs can significantly increase autonomous activities and reduce inquiry behavior. A certain dose of antipsychotic drugs can reduce inquiry behavior without affecting voluntary activities.
The elevated plus maze (Elevated Plus Maze)
The elevated cross maze examines the anxious state of animals by using animal exploration characteristics of new and different environments and fear of high open arms. The elevated cross maze has a pair of open arms and a pair of closed arms. The elevated cross maze is higher than the ground, which is equivalent to standing on a cliff, causing fear and anxiety in the subjects. The elevated plus maze is widely used in the fields of new drug development, pharmacology, toxicology, preventive medicine, neurobiology, animal psychology, and other fields of science-research and computer-assisted instruction. It is an anxiety for medical colleges and research institutions. Classical experiments in depression research.
The animal is placed in the center of the apparatus and observed for a set time. Measurements compare the include total time spent in the open and closed arms (and central platform) as well as entries into the open and closed arms.
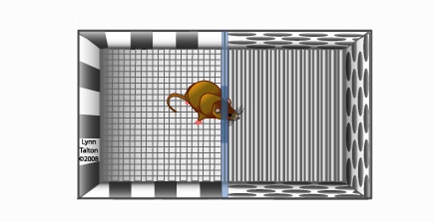
6. Black and white box experiment ( light dark box )
 The subject is placed in the dark portion of the box for a set period of acclimation time. At the end of this period, a door separating the two compartments is opened. The amount of time that the subject takes to emerge fully from the enclosed area Into the open area is measured.
7. Social interaction experiment
The subject is habituated to the test chamber and allowed to freely explore for a set time. A novel animal is placed in one of the two enclosures, and the percentage of time the mouse spends in the section with the novel animal is compared to the time Spent in the section with the empty enclosure. In a later session, the time spent with the same animal might be compared to time spent with a newer, more novel animal.
8. The conditioned place preference (Conditioned Place Preference)
  The Conditional Placement Preference Experiment (CPP) experiment is a classical experimental model for evaluating the mental dependence of drugs. In this experiment, experimental animals (rats, mice) were placed in a white observation area of ​​a conditional position preference box, and psychoactive drugs were administered, and then the activity of the experimental animals in the black and white areas of the conditional position preference box was observed. There is a small door between the white area, the black area and the gray area where the animals can shuttle freely. Each time an animal is in the dosing zone, a positional preference for the black and white regions is exerted by the drug-rewarding effect, the extent of which is related to the mental dependence of the drug.
A drug is injected and the subject is introduced to distinctive environment A. This procedure is repeated for several trials. During these conditioning trials the animal develops an association between the subjective state produced by the drug (often drugs that produce mood elevation or euphoria in humans And the contextual cues present while the drug is active. To test the conditioning, the animal is placed in an apparatus with drug-related cues in one compartment and neutral cues in the other. nbsp; If conditioning occurred, the animal will move toward The compartment containing the drug-related cues.
In a Conditioned Place Preference experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with drug-related cues, and a compartment with neutral cues. If the conditioning was successful for positive, reinforced drug states They should spend more time in the compartment with drug-related cues.
In a Conditioned Place Aversion experiment, subjects are returned to an apparatus were they can freely move between a compartment in which they were conditioned with an aversive stimulus, such as a shock;. And a compartment with neutral cues If the aversive conditioning was successful, They should spend more time in the compartment with neutral cues.
9. Forced Swim (force swim test), the tail suspension test (tail test)
Since some mutations cause a deficit in swimming ability, the forced swim test can be used to demonstrate normal swimming and floating ability. The test is most frequently used to examine the "learned helplessness" response common in animal models of depression.
The subject is suspended by the tail for a set interval the percentage of time the subject spends still versus moving is examined for evidence of the "learned helplessness" response common in models of depression.
The tail suspension experiment is mainly used for the study of antidepressant, sedative and analgesic drugs. The tail suspension experimental system is suitable for use in rats, mice, or other laboratory animals by hanging the animal's tail to hang its head down, recording a series of parameters during the desperate state of motion of the animal in the environment.
10. Conditional fear experiment (fear conditioning)
Conditional fear analysis was used for environmentally relevant conditional fear studies in small rodents (large, mouse). Antidepressants and anti-central stimulants can significantly shorten the duration of immobility. During the experiment, the subject was given an acoustic signal, followed by an electric shock stimulus. This training is called conditional training, and the experimental animals perform sound signals or environmental connectivity experiments after the training. Under normal circumstances, rodents will have obvious conditional fear responses to the same environment and different sound signals in different environments, such as standing still.
The Pavlovian Fear Conditioning task allows for the assessment of learning and memory regarding aversive events. The task allows for the simultaneous assessment of learning about simple, unimodal cues and learning about complex, multimodal stimuli such as context. Fear conditioning universally depends on the integrity of The amygdala, but context conditioning is sensitive to manipulations of the hippocampus. This task has been used extensively to demonstrate both genetically based impairments and enhancements in learning and memory.
11. shock and conditional (startle and pre-pulse inhibition)
Basic Startle Response |
In basic startle, startle stimuli of various intensities are presented unexpectedly. Varying startle response and habituation are recorded. |
Pre-Pulse Inhibition |
In Pre-Pulse Inhibition (PPI), the startle stimulus is paired with a predictive cue. In normal subjects, the "pre-pulse" cue reduces the startle amplitude. This inhibition of the startle response is known as PPI. Humans and animal models Of several disease states are known to have pre-pulse inhibition deficits, including schizophrenia, Alzheimer's, and PTSD. |
Fear-Potentiated Startle |
In Fear-Potentiated Startle, the subjects are trained to associate a neutral stimulus, such as a light cue, with an aversive stimulus. When the startle response is tested in the presence of the light cue, the startle amplitude should be potentiated, or increased . |

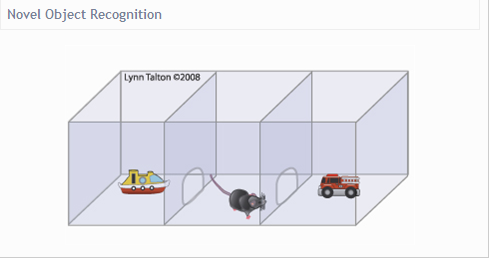
12. Novel object recognition
The subject is habituated to the test chamber and allowed to freely explore for a set time.
A novel object is placed in one of the two enclosures, and the percentage of time the mouse spends in the section with the new object is compared to the time spent in the section with the empty enclosure. In a later session, the time spent with The same object might be compared to time spent with a newer, more novel object.
Surgical Face Mask,Mouth Mask Medical,Surgical Mouth Mask,Disposable Surgical Face Mask
Ningbo Carest Medical Instrument Co.,ltd , https://www.carestmed.com