Culture techniques of the yellow-edge shell turtle
2025-08-18 00:03:06
The yellow-rimmed shell turtle, known for its high economic value, is highly sought after for both culinary and medicinal purposes. Its meat is tender, flavorful, and believed to have nourishing properties that balance yin and yang, aid in detoxification, and even offer anti-cancer benefits. Due to these qualities, it has become one of the most popular species for health and disease prevention. In China, medical professionals primarily use this turtle as a raw material to produce "broken plate turtles" and "broken plate injections," which are effective in treating conditions such as tuberculosis, herpes hemorrhage, and chemotherapy-induced leukopenia.
In addition to its medicinal value, the yellow-rimmed shell turtle is also prized for its aesthetic appeal. Its elegant appearance and gentle nature make it a beloved pet among many people. However, due to overexploitation and habitat loss, wild populations have drastically declined in recent years, creating a significant gap between supply and demand. As a result, prices have soared—rising from 180 yuan per kilogram in 1995 to 450–550 yuan today, with an upward trend continuing. This growing demand has made artificial breeding of the yellow-rimmed shell turtle a promising and profitable venture.
**Morphological Features:**
The yellow-rimmed shell turtle is easily recognizable by its high, dome-shaped carapace, which is nearly half the length of the body. The head is olive-green with a distinct yellow "U"-shaped marking behind the eyes, and the eyes are large with clear tympanic membranes. The carapace ranges from red to brown-red, with a pale yellow central stripe. Each scute shows concentric patterns, while the plastron is dark brown and connected to the carapace via a flexible ligament. The limbs are gray-brown, slightly flattened, with visible scales. Males can be distinguished from females by their more pointed carapace, longer tail, and more elongated body shape, whereas females tend to have a broader back and shorter tail.
**Habitat and Behavior:**
In the wild, these turtles prefer forest edges, shrubs, and rocky areas in hilly regions, often hiding under rocks or in tree crevices. They are nocturnal and prefer quiet environments. Unlike many other turtles, they are bold and not afraid of humans, often showing curiosity and even forming bonds with their owners. They are semi-aquatic and cannot survive in deep water. Their activity patterns change with temperature: they are more active during midday when temperatures are between 18–22°C, and more active at night when temperatures rise to 25–34°C. During the rainy season, they may remain outside their shelters. From December to March, they enter hibernation when temperatures drop below 19°C, emerging again when it reaches 15°C.
**Breeding Habits:**
Yellow-rimmed shell turtles typically mate from mid-April to late October. Males actively court females, sometimes circling them or blocking their movement. After mating, females lay 2–4 eggs per clutch, usually in sandy or loose soil, between May and September. The eggs are oval, measuring about 40–46 mm in length and 20–26 mm in width, with a weight ranging from 8.5 to 20.1 grams. Artificial incubation can be done using a wooden box filled with coarse sand, maintaining a humidity level of around 80% and a temperature of approximately 30°C. Hatchlings emerge after 50–60 days.
**Turtle Pond Construction:**
For artificial breeding, ponds should include both land and shallow water areas. The water depth should not exceed two-thirds of the turtle’s shell height, allowing for easy access. A suitable setup includes nesting areas, feeding zones, open spaces for exercise, and a small pool for drinking and swimming. Providing vegetation helps mimic natural habitats, promoting better growth and reproduction.
**Feeding and Management:**
These turtles are omnivorous, consuming a variety of animal and plant-based foods such as fish, earthworms, fruits, and vegetables. Feeding should be done in the morning or evening, with portions accounting for 3–5% of the turtle’s body weight. It's important to maintain clean water and regularly disinfect the environment. Adding vitamins like C and E can support overall health, while antibiotics such as terramycin help prevent diseases.
**Disease Prevention:**
Although generally hardy, these turtles can suffer from digestive issues if fed poor-quality food. Regular cleaning, disinfection, and the addition of antibiotics to feed can significantly reduce the risk of illness. During hot seasons, shade structures are essential to keep the environment cool, while in winter, soft sand or hay provides ideal hibernation conditions.
With its unique characteristics, high market value, and relatively low maintenance requirements, the yellow-rimmed shell turtle offers great potential for sustainable farming and conservation efforts.
solubility H2O: 50 mg/mL
form powder
color Dark cream powder
Odor Odorless
PH 6.5-7.5 (2% in H2O)
Water Solubility Soluble in water. Insoluble in alcohol.
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive & Hygroscopic
EPA Substance Registry System Peptones (73049-73-7)
Peptone,Yeast extract,L-Glutamine,L-tryptophan,L-alanine,L-aspartic acid,L-methionine,L-threonine,Xanthan gum,Gellan gum,Bovine,serum albumin,Trishydroxymethylaminomethane,IPTG,Sodium pyruvate
Peptone Basic Information
CAS: 73049-73-7
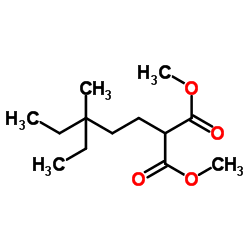
MF: C13H24O4
MW: 244.32726
EINECS: 615-895-9
Mol File: 73049-73-7.mol
Peptone Structure
solubility H2O: 50 mg/mL
form powder
color Dark cream powder
Odor Odorless
PH 6.5-7.5 (2% in H2O)
Water Solubility Soluble in water. Insoluble in alcohol.
Sensitive Moisture Sensitive & Hygroscopic
EPA Substance Registry System Peptones (73049-73-7)
Peptone,Yeast Extract,L-Glutamine,L-Tryptophan,L-Alanine,L-Aspartic Acid,L-Methionine,L-Threonine,Xanthan Gum,Gellan Gum,Bovine,Serum Albumin,Tris Hydroxymethyl Aminomethane,Iptg,Sodium Pyruvate
Shandong YingLang Chemical Co.,Ltd , https://www.sdylhgtrade.com